Fiscal policy and economic governance
Slovenia's multiannual fiscal and economic policy guidelines are set out in the Medium-Term Fiscal and Economic Policy Framework, which is also the basis for annual budgetary planning and the preparation of the Draft Budgetary Plan.
Fiscal rule
The fiscal rule is a budgetary rule aimed at ensuring the sustainability of public finances. In 2013, the National Assembly adopted a constitutional act amending Article 148 of the Constitution. This amendment constitutionally defined the so-called fiscal rule, stating that the revenues and expenditures of the state budgets must be balanced over the medium term without borrowing, or that revenues must exceed expenditures.
In July 2015, the National Assembly adopted the implementing Act on the Fiscal Rule, which more specifically defines how the obligation set by the highest legal act of the state would be implemented in practice. The law was largely based on the European Union (EU) fiscal rules prior to the 2024 reform. Therefore, in light of recent changes to the EU’s economic governance framework, a new Fiscal Rule Act (ZFisP-1) was adopted in March 2025.
To facilitate the conduct of fiscal policy and eliminate inconsistencies that emerged in the planning and monitoring of fiscal rule implementation, ZFisP-1 aligns the concepts of national legislation with EU fiscal rules. As at the EU level, the key medium-term document in ZFisP-1 is the Medium-Term Fiscal-Structural Plan, and the national fiscal rule is defined in coordination with the updated EU fiscal rules.
ZFisP-1 also stipulates that an annual progress report must be prepared each April. This report serves as a key document for monitoring the implementation of commitments from the Medium-Term Fiscal-Structural Plan. Furthermore, ZFisP-1 defines the procedure in case of deviations from the fiscal rule and the conditions under which it is permissible to deviate from the principle of medium-term balance, in line with EU-level solutions.
European Semester
Economic policy measures and national objectives are linked to the EU's common objectives. To achieve these common objectives, the European Commission has set up an instrument called the European Semester, which aims to coordinate economic, fiscal and social policies at EU level. This ensures budgetary discipline in Member States, promotes structural reforms to increase productivity, monitors measures to reduce unemployment and social inequalities, and identifies macroeconomic imbalances in countries.
The European Semester process involves analysing key national structural documents and country-specific recommendations and monitoring their implementation.
The renewed Stability and Growth Pact, the EU's main tool to ensure economic stability and fiscal discipline, also entered into force in 2024. Member States prepare a National medium-term fiscal-structural plans, which are normally valid for four years. Each spring, countries report on the implementation of the plan in their annual reports.
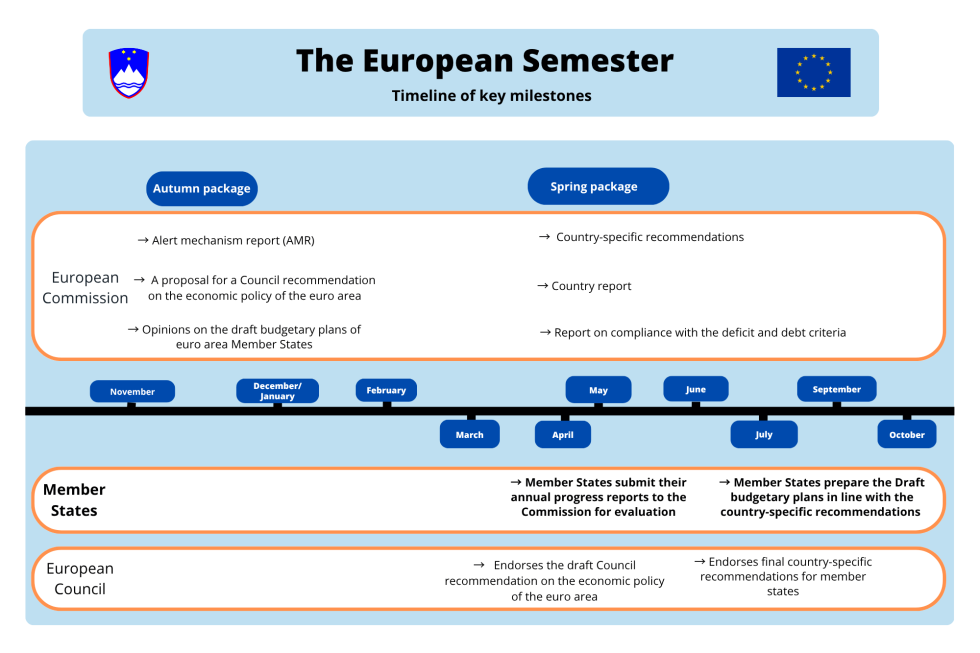
A chronological overview of the European Semester:
The European Semester explained
In November, the European Commission publishes the 'Autumn Package', which launches the new European Semester cycle. The Autumn Package contains the alert mechanism report, the recommendation on the economic policy of the euro area and the draft joint employment report. The Council of the EU then approves the conclusions on the alert mechanism report and adopts the recommendations on economic policy for the euro area. The European Council (heads of state or government) then adopts the conclusions on the alert mechanism report. The joint employment report is discussed and finally adopted by the EU Council.
Member States prepare an annual progress report and send it to the European Commission in April.
In the 'Spring Package', published in May or June, the European Commission presents a proposal for country-specific recommendations and country reports. The proposals for country-specific recommendations are discussed in the different Council formations. The final country-specific recommendations are agreed by the Council of the EU and endorsed by the European Council. They are then formally adopted by the Council of the EU.
Member States take the recommendations into account when deciding on their national budgets for the following year and when adopting their draft budgetary plans. Member States submit these to the European Commission by 15 October each year.
Medium-term fiscal and structural plan
Under the EU's reformed fiscal rules, countries prepare a Medium-Term Fiscal and Structural Plan every four years, setting out fiscal targets and key reforms and investments that contribute to achieving the targets or address specific recommendations under the European Semester and other EU priorities. The fiscal targets are set on the basis of growth of so-called net expenditure, which is fixed for the plan period and should ensure the sustainability of public debt in the medium term and keep the general government deficit below the reference limit of 3% of gross domestic product. Net expenditure here represents all general government expenditure, excluding interest expenditure, discretionary revenue measures, expenditure on EU programmes, expenditure on unemployment benefits and one-off and other temporary measures. The medium-term fiscal and structural plan is a key instrument of the country's economic policy, alongside the annual budgets, and sets out the government's programme and policy priorities for the future. It is verified by the European Commission and endorsed by the Council of the EU.
The medium-term fiscal-structural plan defines the planned fiscal policy, with the growth of the so-called net expenditure fixed over the period of the plan, as well as key reforms and investments in response to country specific recommendations under the European Semester and common EU priorities. The adequacy of the plan is checked by the European Commission and approved by the Council of the EU. The first medium-term fiscal-structural plan must be submitted to the European Commission and the Council of the EU for endorsement by 20 September or 15 October 2024 at the latest.
-
Medium-term fiscal-structural plan
Strategies and programmes
Draft budgetary plan
In accordance with the provisions for monitoring and assessing draft budgetary plans and ensuring the correction of excessive deficits in euro area Member States, all Member States transmit their draft budgetary plans to the European Commission by 15 October at the latest. They present a detailed description of the implementation of the fiscal policy strategy for the following year and concrete expenditure and revenue measures that will ensure compliance with the fiscal targets in terms of growth in net expenditure. The planned net expenditure should not exceed the growth in net expenditure set out in the Medium-Term Fiscal and Structural Plan, and may be lower. While the Medium-Term Fiscal and Structural Plans are strategic documents, the Draft Budget Plans are more executive or operational in nature.
-
Draft budgetary plan
Plan- Draft Budgetary Plan 2025 (pdf, 1.1 MB)
- Draft Budgetary Plan 2024 (pdf, 1.1 MB)
- Draft Budgetary Plan 2023 (pdf, 598 KB)
- Draft Budgetary Plan 2022 (pdf, 998 KB)
- Draft Budgetary Plan 2021 (pdf, 1.1 MB)
- Draft Budgetary Plan 2020 – Addendum (pdf, 132 KB)
- Draft Budgetary Plan 2020 (pdf, 822 KB)
- Draft Budgetary Plan 2019 – update (pdf, 1.1 MB)
- Draft Budgetary Plan 2019 (pdf, 616 KB)
Annual progress report
The Annual Progress Reports serve as key documents in monitoring compliance with the fiscal targets, reforms and investments set out in the Medium-Term Fiscal and Structural Plan. They also report on the implementation of measures to address country-specific recommendations and common EU priorities. Countries submit the report to the European Commission by the end of April each year.
Technical Support Instrument
The European Commission's Technical Support Instrument supports the implementation of reforms to sustain growth and increase resilience in Member States. Technical support is designed to prepare and implement measures and reforms in the context of the European Semester, the economic governance process or measures related to the implementation of Slovenia's priorities and Union policies.
The TSI provides tailor-made technical support to Member States for the design and implementation of reforms and other forms of action, analysis and strategies. Such technical support is fully funded by the European Commission programme and does not require national co-financing.
The Ministry of Finance is the national coordinator for the application of projects under the TA Facility.
The European Commission launches a new call for projects each year, which closes at the end of October. The Ministry of Finance, as the national coordinator of the TSI projects, is the entry point for the final project proposals, which are then forwarded to the Commission. Prior to this, the project proposals are also shared with the Government of the Republic of Slovenia. The national deadline for the submission of project proposals is the end of September and the deadline for the submission of project proposals to the Commission is the end of October.
For information on the Technical Support Instrument, contact the Ministry of Finance: